3KG/h Ozone Generator Water Treatment Application Plan
# 3KG/h Ozone Generator Water Treatment Application Plan
## 1. Technical Background and Equipment Overview
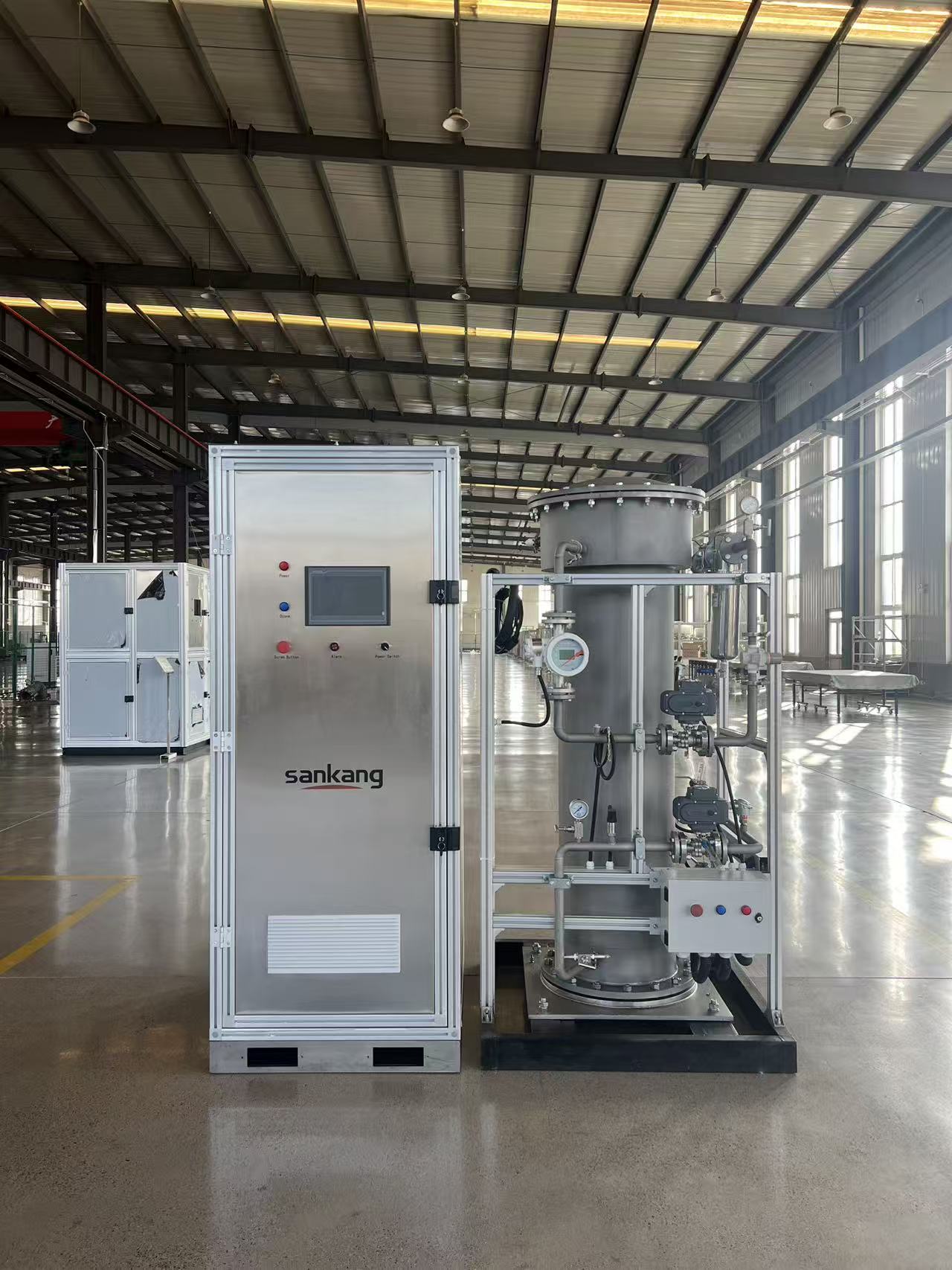
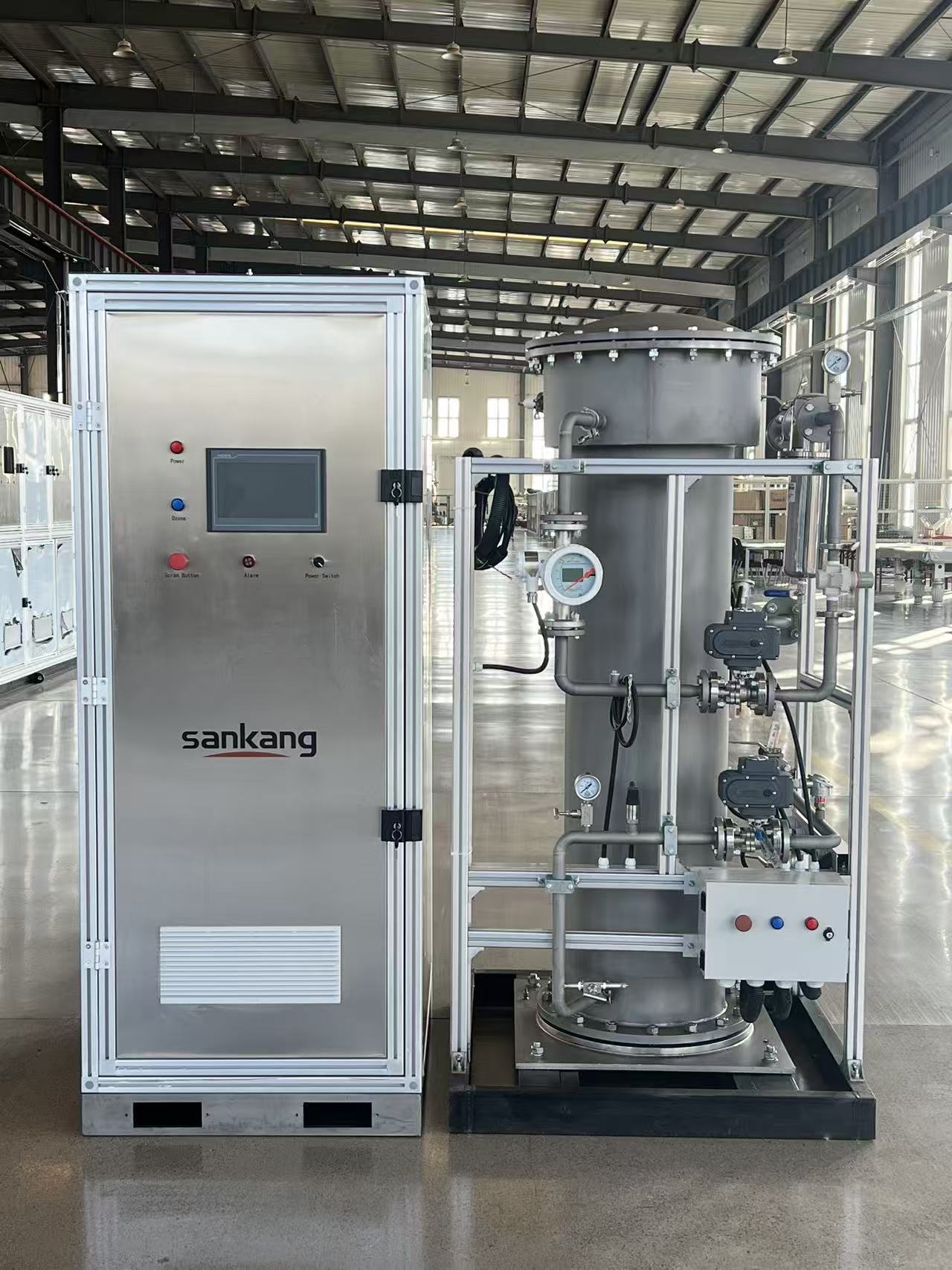
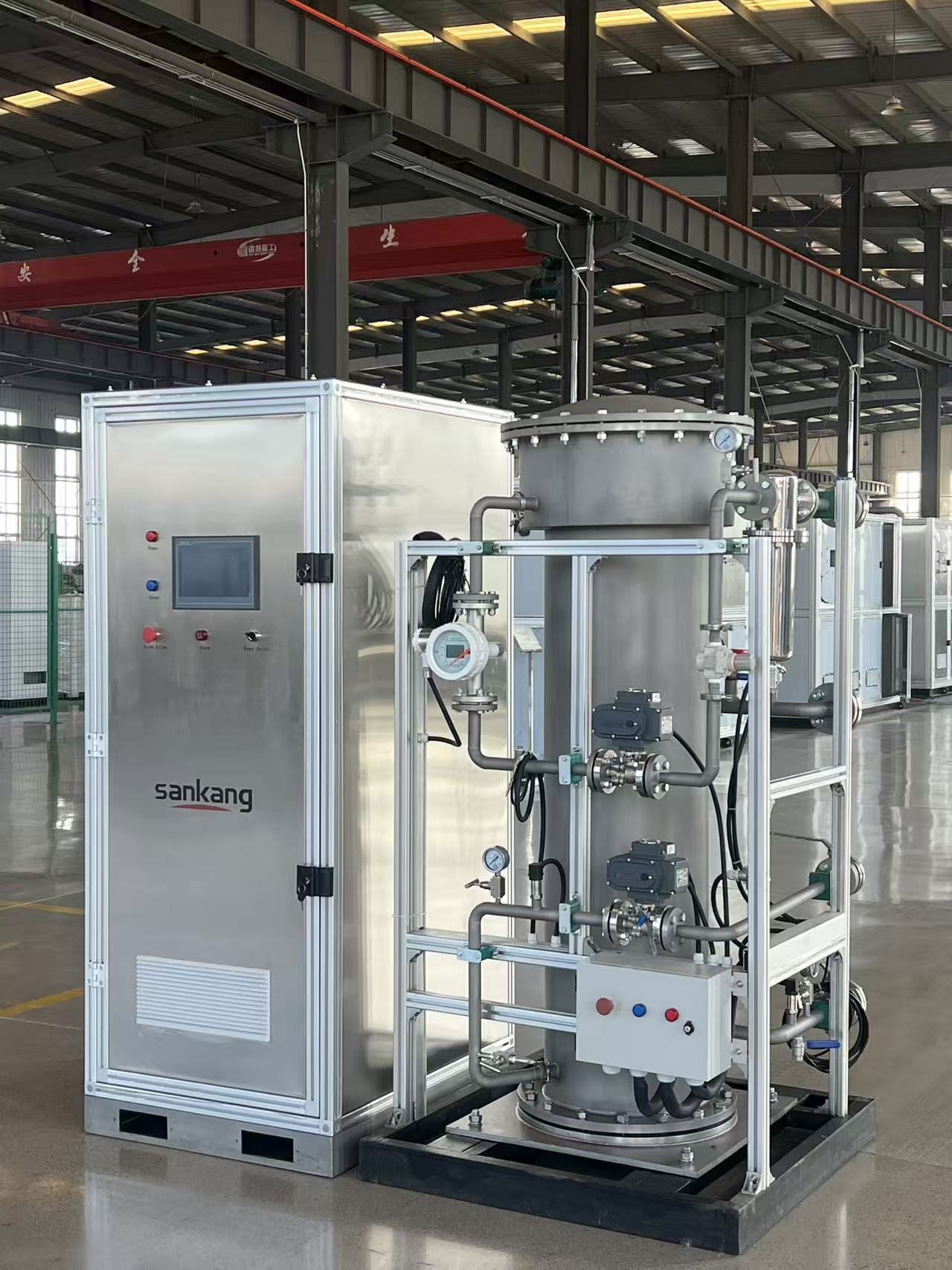
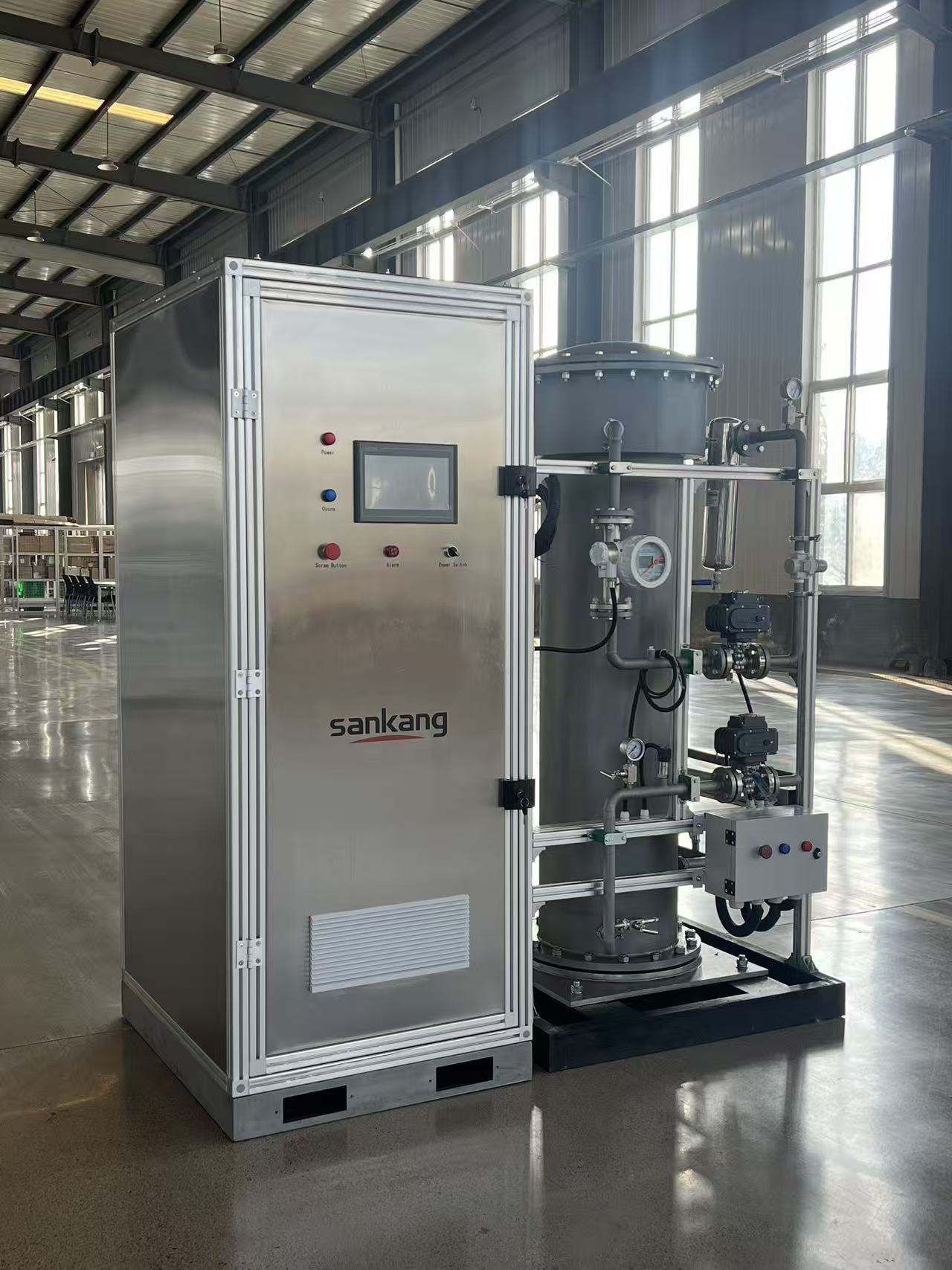
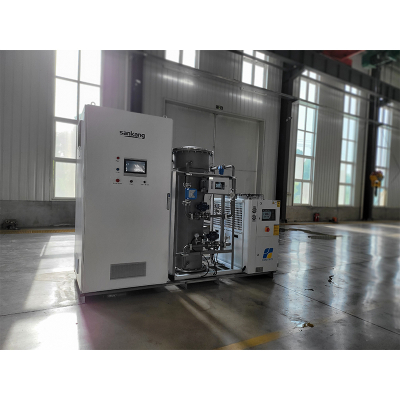
Ozone (O₃), as a strong oxidizer, has an oxidation capacity 1.5 times that of chlorine and shows significant advantages in the field of wastewater treatment. The 3KG/h ozone generator, as an industrial-grade device, converts oxygen into ozone through corona discharge. Its core components include the ozone generation chamber, oxygen production system, cooling module, and intelligent control system. Taking a certain brand of equipment as an example, its ozone concentration can reach up to 12wt%, with a power consumption of ≤7kWh/kgO₃. Equipped with a water-cooling circulation system, it can operate stably in environments from 5-40℃, making it suitable for large-scale water treatment applications.
Core Process Flow Design
### 1. Pretreatment Stage
Pretreatment should be targeted to remove suspended solids, grease, and large molecular organic matter according to different water quality characteristics. For example, in the treatment of dyeing and printing wastewater, fiber debris needs to be intercepted by screens, and ink particles separated using flotation; for electroplating wastewater containing heavy metals, a coagulant should be added to precipitate heavy metal ions. The efficiency of pretreatment directly affects ozone utilization, and experimental data show that pretreated wastewater can achieve more than a 30% increase in ozone oxidation efficiency.
### 2. Ozone Dosing and Mixing System
3KG/h ozone generator uses a Venturi injector combined with a packed tower process:
- Venturi Injector: Uses high-speed airflow to generate negative pressure, thoroughly mixing ozone gas with wastewater. Contact time reaches 5-8 seconds, suitable for low-concentration organic matter degradation.
- Packed Tower Reactor: The tower is filled with multi-faceted hollow sphere packing. Wastewater is sprayed from top to bottom while ozone flows counter-currently from bottom to top, expanding the liquid film surface area 5-8 times, significantly enhancing ozone mass transfer efficiency. A petrochemical wastewater treatment case showed that this process achieved a COD removal rate of 68% and a color removal rate exceeding 95%.
### 3. Advanced Treatment and Off-Gas Control
Ozone oxidation requires two levels of post-treatment:
- Gas-Liquid Separation: Uses combined gravity sedimentation and centrifugal separation technology to recover unreacted ozone, with a recovery rate above 92%.
- Off-Gas Destruction: Remaining ozone is decomposed into oxygen through a catalytic oxidation device (containing MnO₂/Al₂O₃ catalyst) to ensure emission concentrations are <0.1 ppm, meeting the GB3095-2012 Ambient Air Quality Standards.
- Post-Treatment: For refractory organic matter, activated carbon adsorption or biofilter processes can be used in combination. For example, a pharmaceutical wastewater treatment project employed an "ozone oxidation followed by biodegradation" process combination, resulting in effluent COD stably below 50 mg/L, meeting the Class A standard of the "Urban Sewage Treatment Plant Pollutant Discharge Standards."
## . Typical Application Scenarios and Parameter Configuration
### 1. Industrial Wastewater Treatment
- Printing and Dyeing Wastewater: Treatment scale of 500 m³/d, ozone dose of 15 mg/L, contact time of 15 minutes, achieving 90% degradation of reactive dyes, effluent color less than 10 times.
- Pharmaceutical Wastewater: For high-concentration organics (COD > 2000 mg/L), the "Ozone Catalytic Oxidation MBR" process is used, with an ozone dose of 50 mg/L and a reaction time of 30 minutes, achieving over 85% COD removal.
### 2. Municipal Sewage Treatment
- Advanced Treatment: After the conventional AAO process, an ozone contact tank is added with a dose of 10 mg/L, removing more than 80% of trace organics, and the effluent meets the "Standards for Drinking Water Quality" requirements.
- Sludge Reduction: Ozone oxidation breaks down sludge cell structures, reducing sludge production by 30% while improving sludge dewatering performance.
### 3. Special Applications
- Medical Wastewater: For wastewater containing pathogenic microorganisms, an ozone dose of 20 mg/L with a contact time of 20 minutes achieves >99.99% E. coli inactivation, complying with the "Discharge Standards of Water Pollutants for Medical Institutions".
- Swimming Pool Water Treatment: Using a cyclic dosing method to maintain a residual ozone concentration of 0.2-0.5 mg/L, effectively inhibiting algae growth while avoiding the formation of chlorinated disinfection by-products.
## . Economic Efficiency and Operation & Maintenance Management
### 1. Cost Analysis
Taking a 3KG/h device as an example:
- Electricity consumption: Calculated at 7 kWh/kg O₃, running 10 hours a day costs about 210 RMB (electricity price 0.3 RMB/kWh).
- Consumables: Ceramic discharge tubes have a lifespan of over 20,000 hours, with an annual replacement cost of about 50,000 RMB; operating costs with an oxygen source are about 40% lower than with an air source.
- Overall cost: The cost to treat 1 ton of wastewater is about 3-5 RMB, which is 25% lower than traditional Fenton oxidation methods.
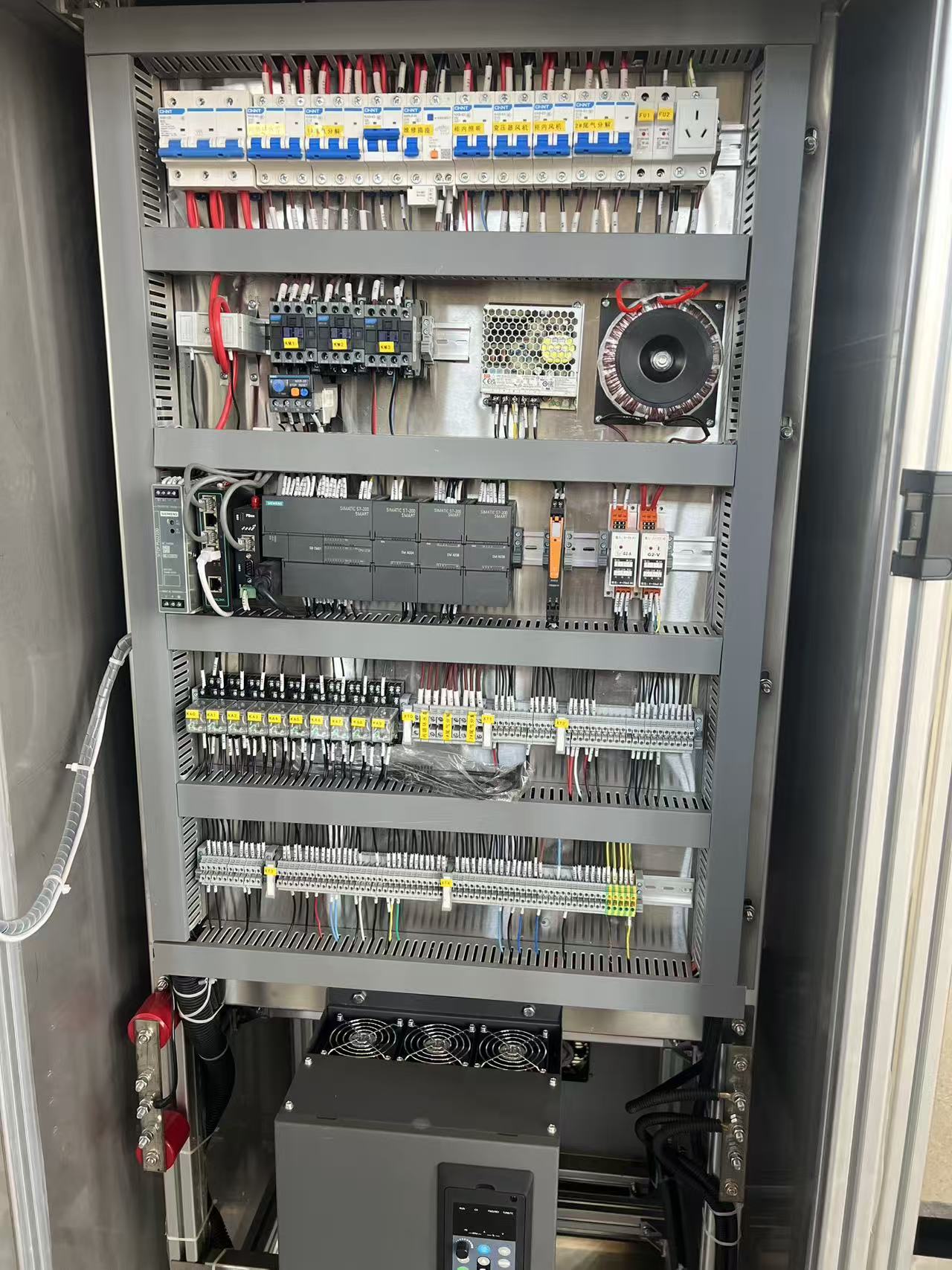
### 2. Intelligent Operation and Maintenance System
The equipment is equipped with a PLC control system, capable of real-time monitoring of:
- Key parameters such as ozone concentration, dosing amount, and contact time
- Operating status such as cooling water temperature and gas source pressure
- Automatic alarm functions (e.g., ozone leakage, voltage abnormalities)
It is recommended to clean the electrodes and maintain the cooling system quarterly, and conduct a comprehensive performance check annually to ensure the equipment lifespan is over 8 years.